Grout lines in pools and flooring systems serve a vital aesthetic and functional role. However, over time, improper material selection, application errors, or environmental factors can lead to grout efflorescence—causing both visual disturbance and potential structural damage like water seepage. In this article, we explore the causes, effects, cleaning methods, and preventive actions for grout efflorescence in detail.
What Is Grout Efflorescence?
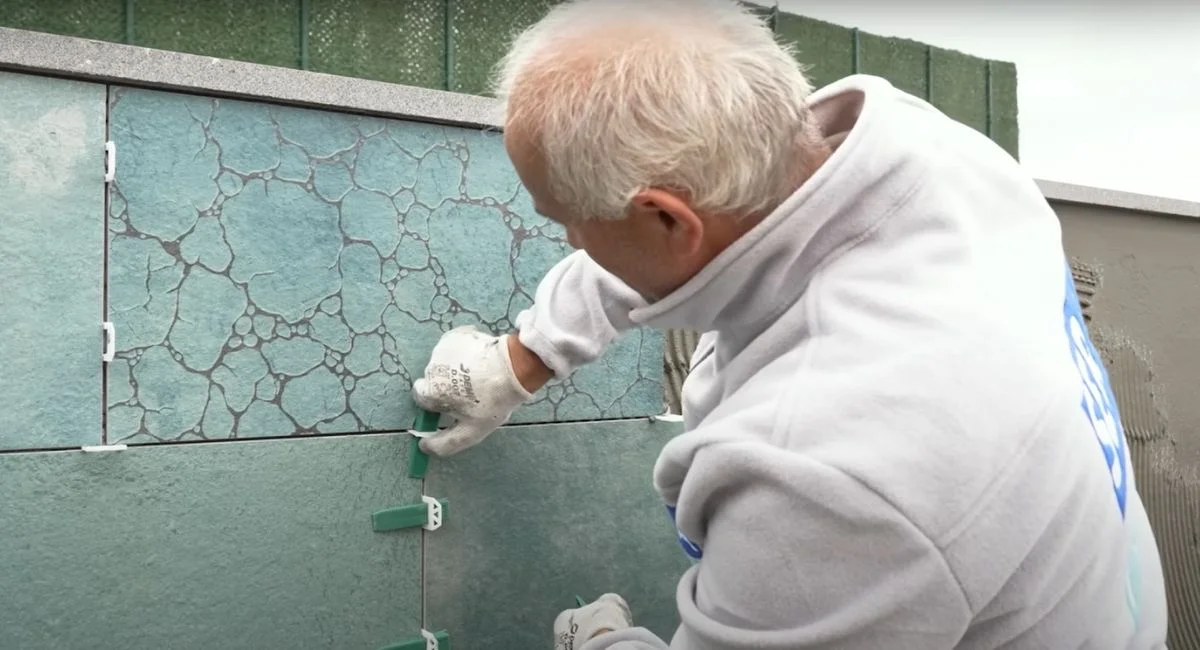
Grout efflorescence refers to aesthetic and structural imperfections that appear along the joints of tiled surfaces. These may present as cracking, crumbling, or discoloration of the grout lines. Grouts are designed to resist water, chemicals, and external factors. Yet, poor application, low-quality materials, or adverse environmental conditions may degrade both the appearance and functionality of the grout over time.
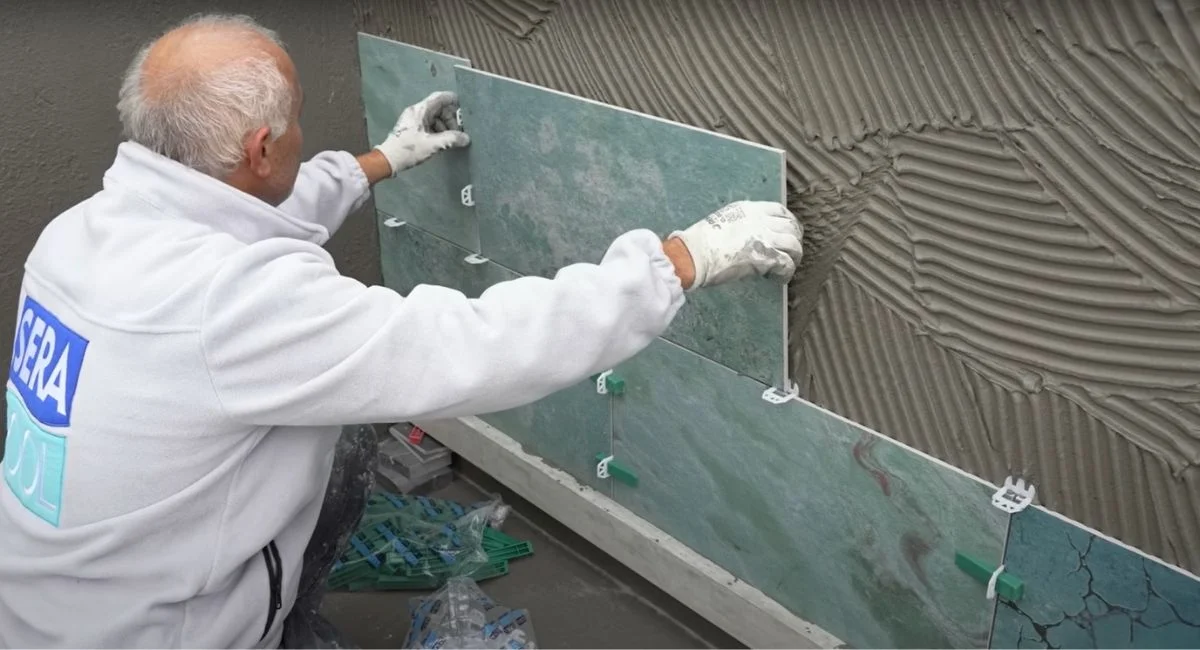

Main Causes of Grout Efflorescence
Grout efflorescence can result from multiple factors, with improper material selection and poor application being the most common. Key causes include:
- Incorrect Material Selection: Grout materials vary in durability. Using low-quality or incompatible grout mixtures often leads to failure. In particular, substandard grouts may lack resistance to water and chemical exposure.
- Poor Surface Preparation and Application: If the grout isn’t applied properly or the surface is inadequately cleaned and prepped, cracks or detachment may occur over time.
- Chemical Exposure and Water pH: Pool water often contains chemicals that gradually erode grout. Imbalanced water pH—whether too acidic or alkaline—can accelerate degradation.
- Environmental Wear: Sunlight, wind, and humidity can reduce the lifespan of grout, resulting in surface imperfections and efflorescence.
Consequences of Grout Efflorescence
Grout efflorescence affects more than just the aesthetics—it may also lead to serious structural concerns:
- Visual Disruption: Efflorescence can tarnish the overall appearance of high-end designs, especially when paired with premium materials like Porcelain Tiles.
- Structural Damage & Water Leakage: Cracked grout lines can allow water to seep into sublayers, potentially compromising waterproofing systems and structural integrity.
- Hygiene and Health Risks: Degraded grout enables contaminants to penetrate, creating a breeding ground for bacteria and other microorganisms.
How to Prevent Grout Efflorescence
Preventing grout efflorescence requires high-quality materials and proper maintenance practices. For long-term performance:
- Use durable, water-resistant materials such as Porcelain Tiles.
- Ensure installation is carried out by skilled professionals, with proper surface preparation and even application.
- Regular cleaning extends the life of grout lines and minimizes efflorescence risk.
- Maintain balanced water pH levels to protect chemical integrity.
How to Clean Grout Efflorescence
Effective grout cleaning relies on using the right products and techniques:
- Use non-acidic cleaners to remove dirt and stains without compromising the material.
- Gently scrub with soft brushes to avoid trapping debris in the joints.
- Choose pH-balanced products, especially cleaners formulated for Porcelain Tiles.
- After cleaning, allow grout to dry thoroughly and avoid water accumulation in the joints.
When and How to Replace Damaged Grout
If efflorescence persists despite cleaning, grout replacement becomes necessary. This is typically done when cracking or disintegration occurs. The process includes:
- Completely removing the old grout and cleaning residual debris.
- Applying a high-quality grout evenly and smoothly.
- Maintaining the new grout properly ensures long-lasting use and reduces the risk of future issues.

Frequently Asked Questions
Why does grout effloresce?
Grout efflorescence typically occurs due to poor material quality, improper installation, unbalanced pH, or external elements such as chemicals or high humidity.
Why does mold form in grout lines?
Mold usually results from prolonged moisture retention and inadequate ventilation. Standing water and lack of cleaning promote mold and mildew growth.
How do you fix frozen grout?
Frozen grout is often caused by extreme cold. Gentle warming or using lukewarm water can help. In severe cases, reapplication might be needed.
How do you remove yellowing from grout?
Yellowing may stem from mineral deposits or dirt. Gently using pH-balanced or specially formulated grout cleaners can help restore color.